Speaker Close
Electrodynamic speakers radiate both sides of their membranes, this operation is called a dipole.
During the forward movement of the diaphragm creates a pressure wave in front of the speaker.
The wave created by the back then called wave of depression.
Failure to take these two waves the effect of the two waves will be canceled as to create some air movement.
A very simple experiment to verify this physical aspect, is a high power speaker (thus able to reproduce high frequencies) the open set on a table with a 50 Hz sinusoidal signal: If we see clearly the movements of the membrane and the sound are very low.
This short-circuit noise is due to dipole operation requires at least placing a screen separating the front and rear in terms of waves produced.
The time spent by air vibrations, which propagate at a speed C (343.4 m / s, 20 ° C) for around a circular screen of diameter D is t = D / C.
The pressures are balanced and cancel each other (there is more noise) when time t coincides with the period T (inverse of the frequency f) of the sound signal T equal to 1 / f = D / C.
Knowing the lowest frequency to produce a good separation between waves forward and backward, can only be obtained when D> c / f.
This imposes a minimum size of the screen on the basis of the lowest frequency to be reproduced.
The following table shows the value of the wavelength of a few frequencies from 20 to 10 000 Hz Speed of sound in air is taken as 340 m / s. The wavelengths are given in meters lower frequencies we want to repeat
Frequency |
wavelength |
Frequency |
wavelength |
20 |
17,00 |
1 000 |
0,34 |
50 |
6,80 |
2 000 |
0,17 |
100 |
3,40 |
5 000 |
0,068 |
200 |
1,70 |
10 000 |
0,034 |
500 |
0,68 |
20 000 |
0,017 |
It follows from this table, to effectively reach the lower frequency of 20 Hz in theory should produce a screen of at least 17 m in diameter.
We also see that for a frequency of 1000 Hz, only have to mount the speaker on a screen of 34 cm in diameter to avoid acoustic short circuit.
To play 5 000 Hz only need a 6.8 inch screen that resembles the overall size of a tweeter that will avoid the phenomenon of diffraction.
Advantages of the bass-reflex box |
Disadvantages of the bass-reflex box |
Functioning very regular speaker). |
the loudspeaker used does not suffer any mediocrity, a model of 30 cm or 38 cm is needed.
|
simple calculation of the volume of the box |
the volume is necessarily large, resulting in a compact cabinet. |
opportunity to let the speaker down low in the grave, rather naturally, and therefore no significant resonance or increase in distortion. |
the yield is generally lower than a bass-reflex, hence the need for a powerful amplifier of excellent quality. |
Montage of a loudspeaker in a bass reflex box
If the speaker is mounted enclosure, its frequency resonance is written:

Fc : Resonance frequency in enclosure (Hz)
F0: resonance frequency in air (Hz)
k: coefficient of stiffness of the suspension of the
membrane (N / m)
S: surface active speaker (dm ²)
V : Volume inside the chamber (dm3)
The damping coefficient at low frequencies of
the enclosure is written:
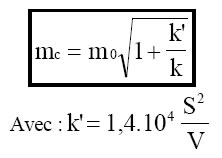
mc: damping coefficient in enclosure
m0: damping coefficient in air
For good results at low frequencies the coefficient
amortization should be between 0.7 and 0.5.